best test to diagnose rotator tear|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff : specialty store They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential .
Autoclave con pompa sommersa Essenziale in caso di pressione dell’acquedotto bassa o variabile. Grazie alla presenza del serbatoio di accumulo acqua, il sistema funge anche da riserva idrica in caso di .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Arrange items inside the autoclave chamber strategically to allow for adequate steam circulation and penetration. Place items in a manner that minimizes air pockets and ensures uniform exposure to steam, optimizing .
Below are 5 easy Physical Therapy tests you can use to identify whether your rotator cuff is compromised or torn. If have someone else at home capable of following simple directions, ask them to help you by applying oppositional force. Otherwise, if you’re home alone, no worries – you can just use your good arm . See more
So to review, I recommend the following tests for a rotator cuff tear: 1. Empty Can Test 2. Drop Arm Test 3. Lag Sign 4. Infraspinatus Test 5. Lift-Off Test If you . See morePhysical Therapists conduct special tests as part of their overall assessment. Before provoking symptoms with orthopedic tests, your PT will gather as much . See more
They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your . If you have pain in your shoulder or can’t lift your arm, you might have a rotator cuff tear. Beyond googling your symptoms and self-diagnosing, consider trying a few of the special tests we PTs use in the clinic to assess a rotator cuff tear. They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential . A doctor might request one of several imaging tests to diagnosis your torn rotator’s cuff such as an x-ray, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging(MRI).
Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are common, especially as you get older. Rest, pain relievers and physical therapy can help. Doctors can diagnose a torn rotator cuff by doing a physical examination, ultrasound, x-ray or MRI. These exams will help them determine the severity of the tear. Pain from a torn rotator. A positive lag sign with external rotation is the best test for full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus and supraspinatus (positive likelihood ratio = 7.2). A positive lag sign with.
centrifuges for honey
Description. When one or more of the rotator cuff tendons is torn, the tendon becomes partially or completely detached from the head of the humerus. In most rotator cuff tears, the tendon is torn away from the bone. Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved.Your doctor will likely order one or more of the following advanced imaging tests to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and determine the extent of the damage: X-ray; MRI; Musculoskeletal ultrasound; CT scan
Rotator cuff injury is a common cause of shoulder pain, especially in older and active people. Tears can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The cause of a rotator cuff tear can be traumatic or attritional. Treatment is typically based on degree of dysfunction, pain, quality of tendons and muscles of.
Symptoms. The pain associated with a rotator cuff injury may: Be described as a dull ache deep in the shoulder. Disturb sleep. Make it difficult to comb your hair or reach behind your back. Be accompanied by arm weakness. Some rotator cuff injuries don't cause pain. When to see a doctor. Your family doctor can evaluate short-term shoulder pain. If you have pain in your shoulder or can’t lift your arm, you might have a rotator cuff tear. Beyond googling your symptoms and self-diagnosing, consider trying a few of the special tests we PTs use in the clinic to assess a rotator cuff tear. They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential . A doctor might request one of several imaging tests to diagnosis your torn rotator’s cuff such as an x-ray, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging(MRI).
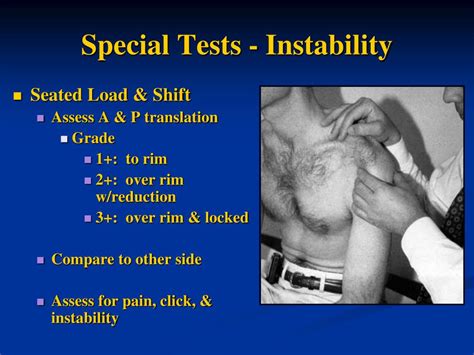
special tests for shoulder instability
Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are common, especially as you get older. Rest, pain relievers and physical therapy can help. Doctors can diagnose a torn rotator cuff by doing a physical examination, ultrasound, x-ray or MRI. These exams will help them determine the severity of the tear. Pain from a torn rotator. A positive lag sign with external rotation is the best test for full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus and supraspinatus (positive likelihood ratio = 7.2). A positive lag sign with.
Description. When one or more of the rotator cuff tendons is torn, the tendon becomes partially or completely detached from the head of the humerus. In most rotator cuff tears, the tendon is torn away from the bone. Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved.Your doctor will likely order one or more of the following advanced imaging tests to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and determine the extent of the damage: X-ray; MRI; Musculoskeletal ultrasound; CT scan Rotator cuff injury is a common cause of shoulder pain, especially in older and active people. Tears can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The cause of a rotator cuff tear can be traumatic or attritional. Treatment is typically based on degree of dysfunction, pain, quality of tendons and muscles of.
centrifugal concentrator stlb 60
shoulder rotator cuff special tests
rotator cuff tear self test
rotator cuff tear physical exam
In Europe, biological monitors are not used routinely to monitor the sterilization process. Inst.
best test to diagnose rotator tear|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff